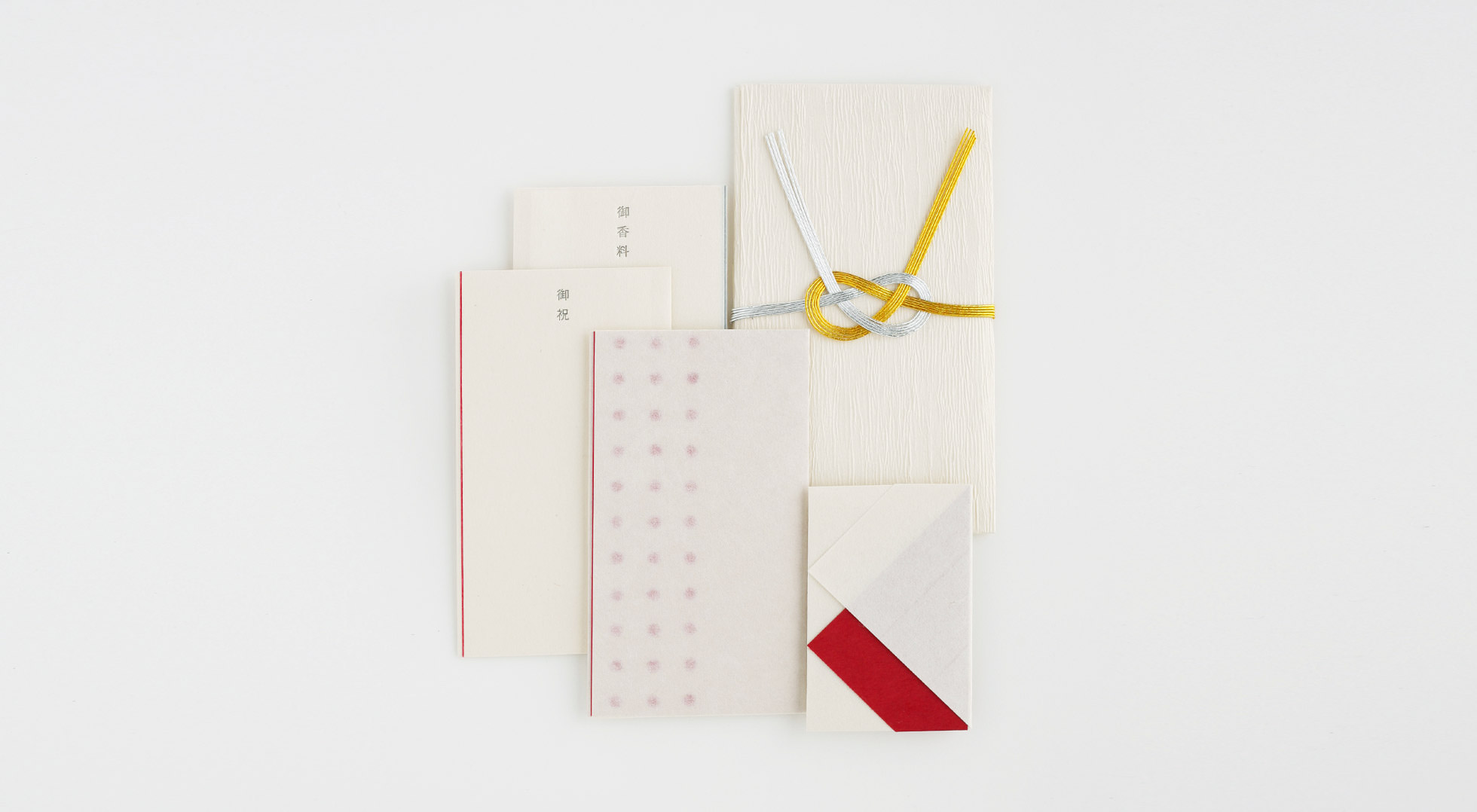
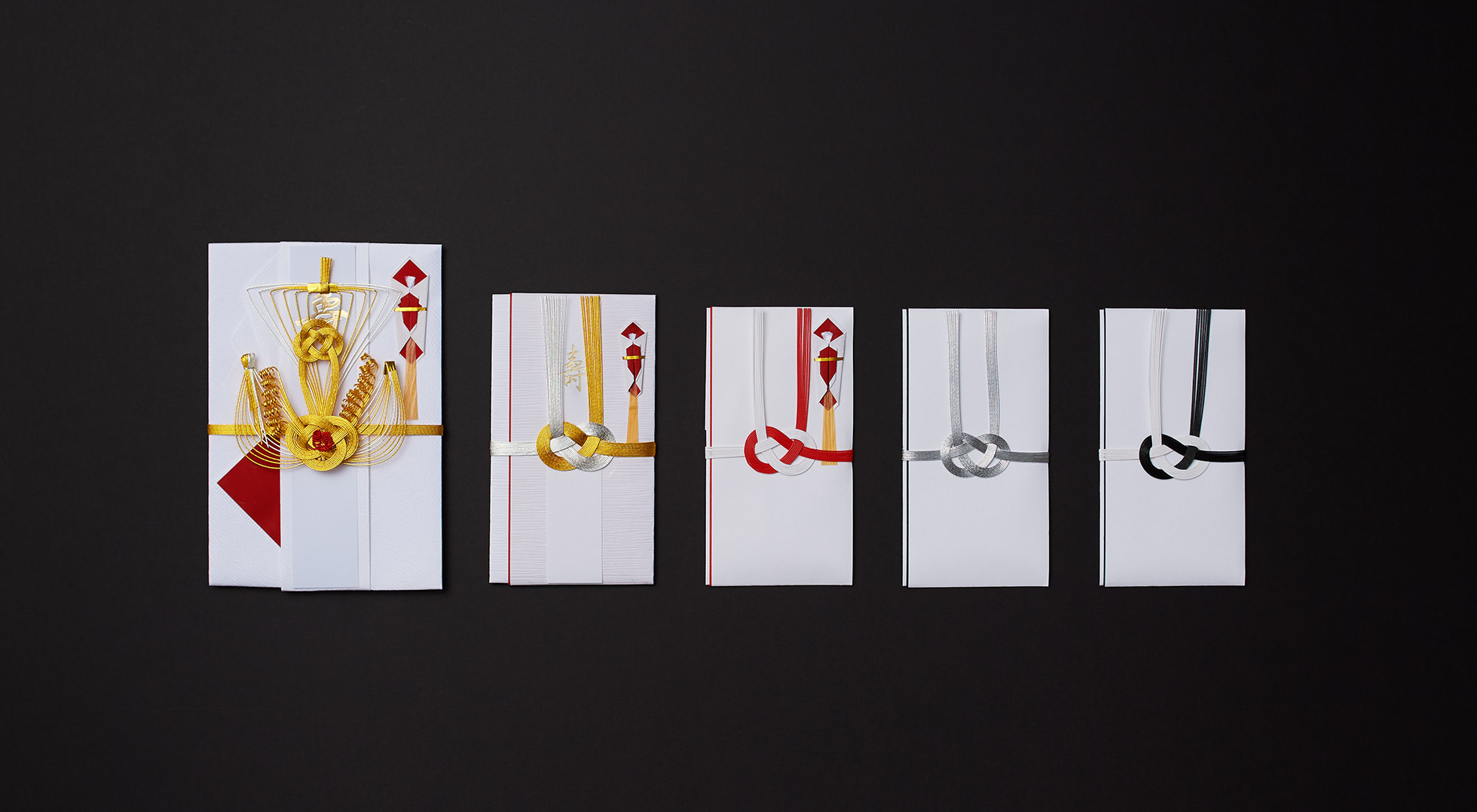
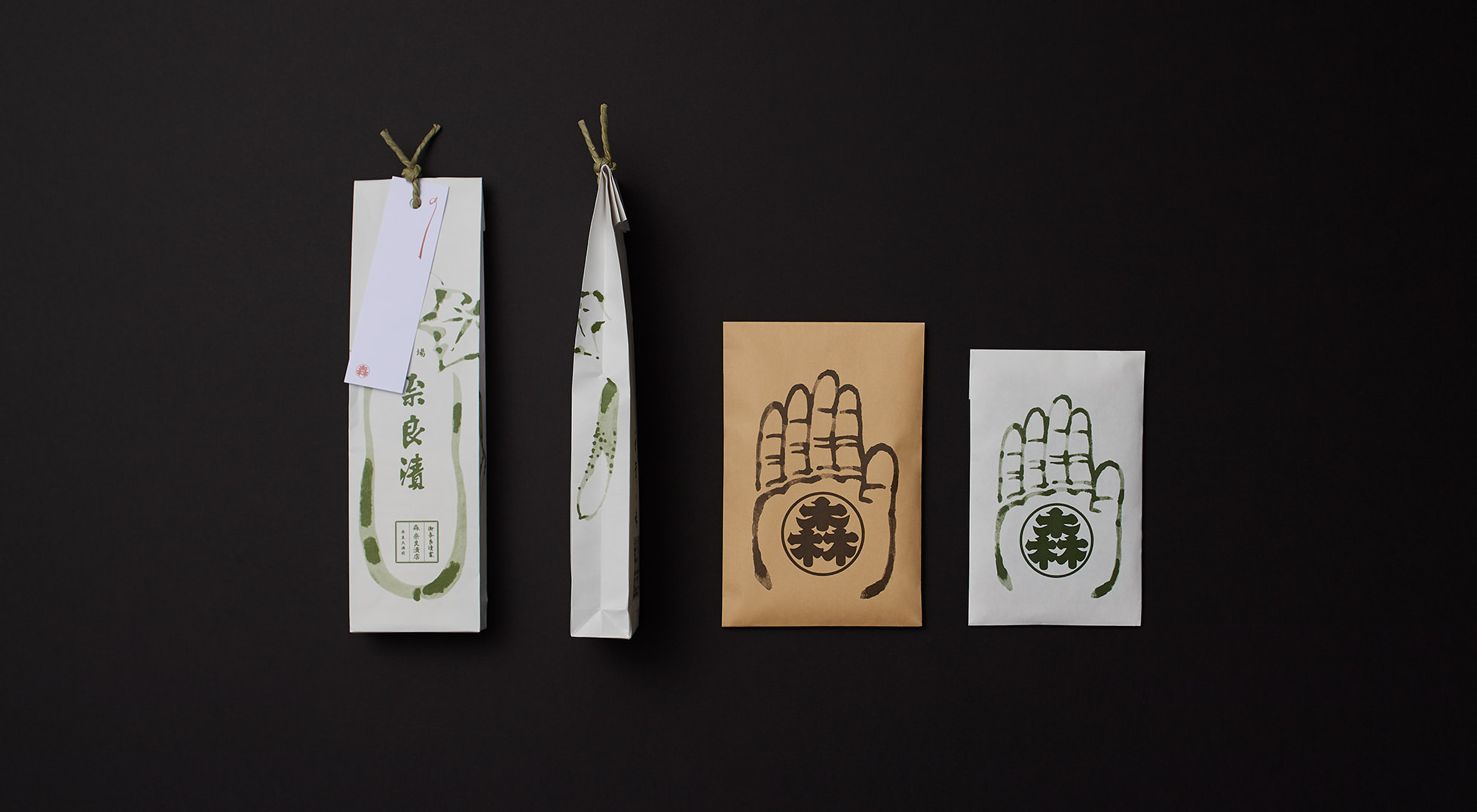
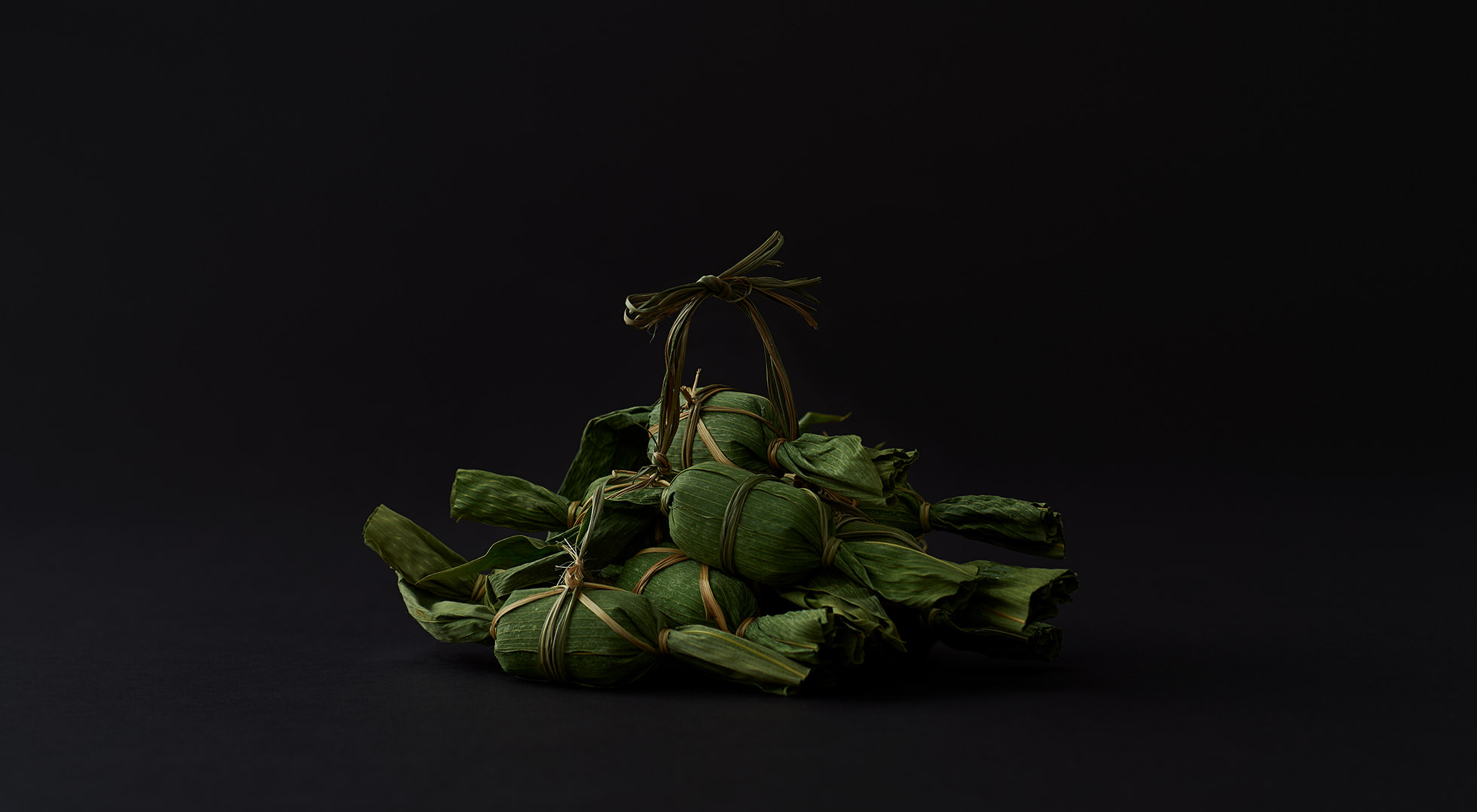
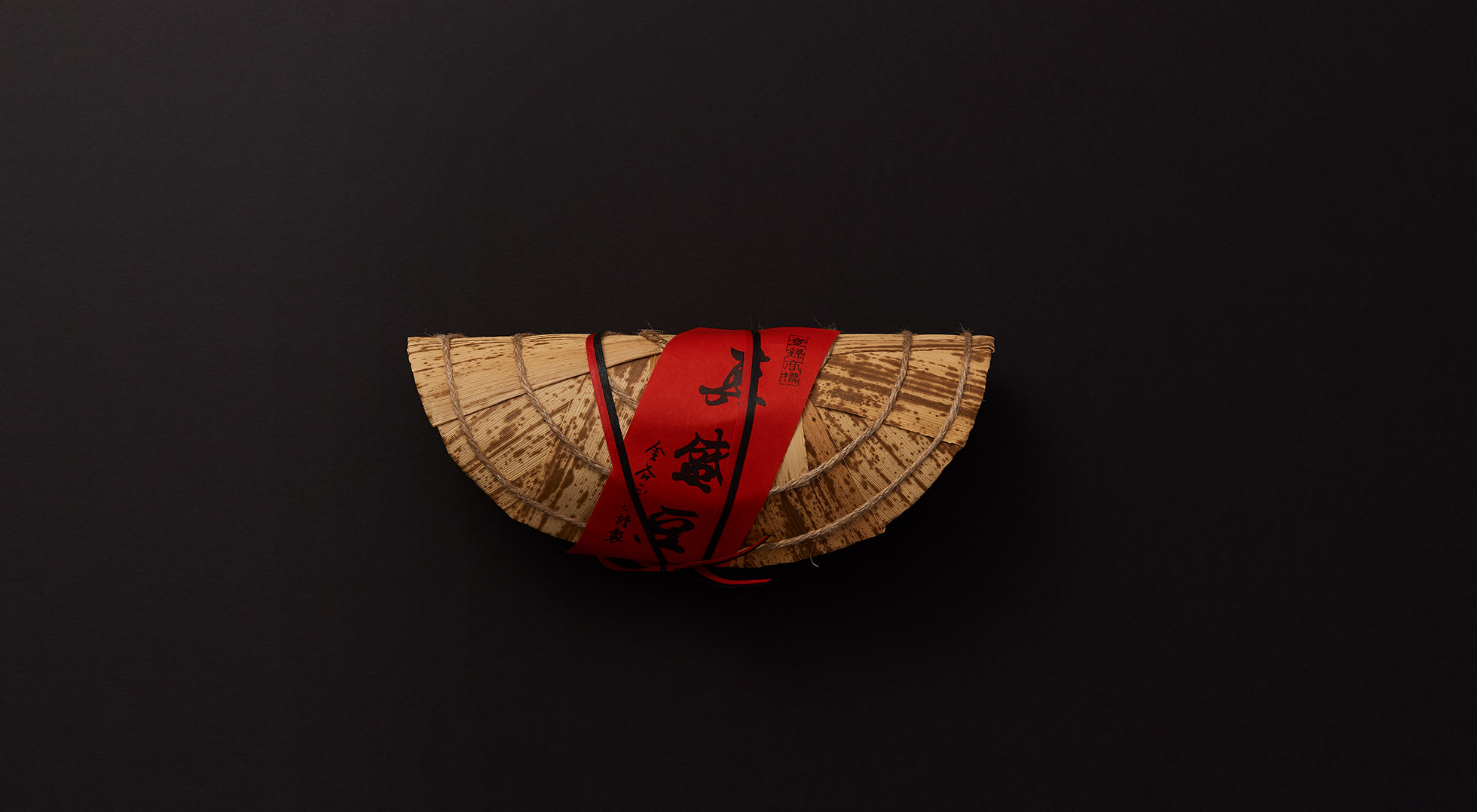
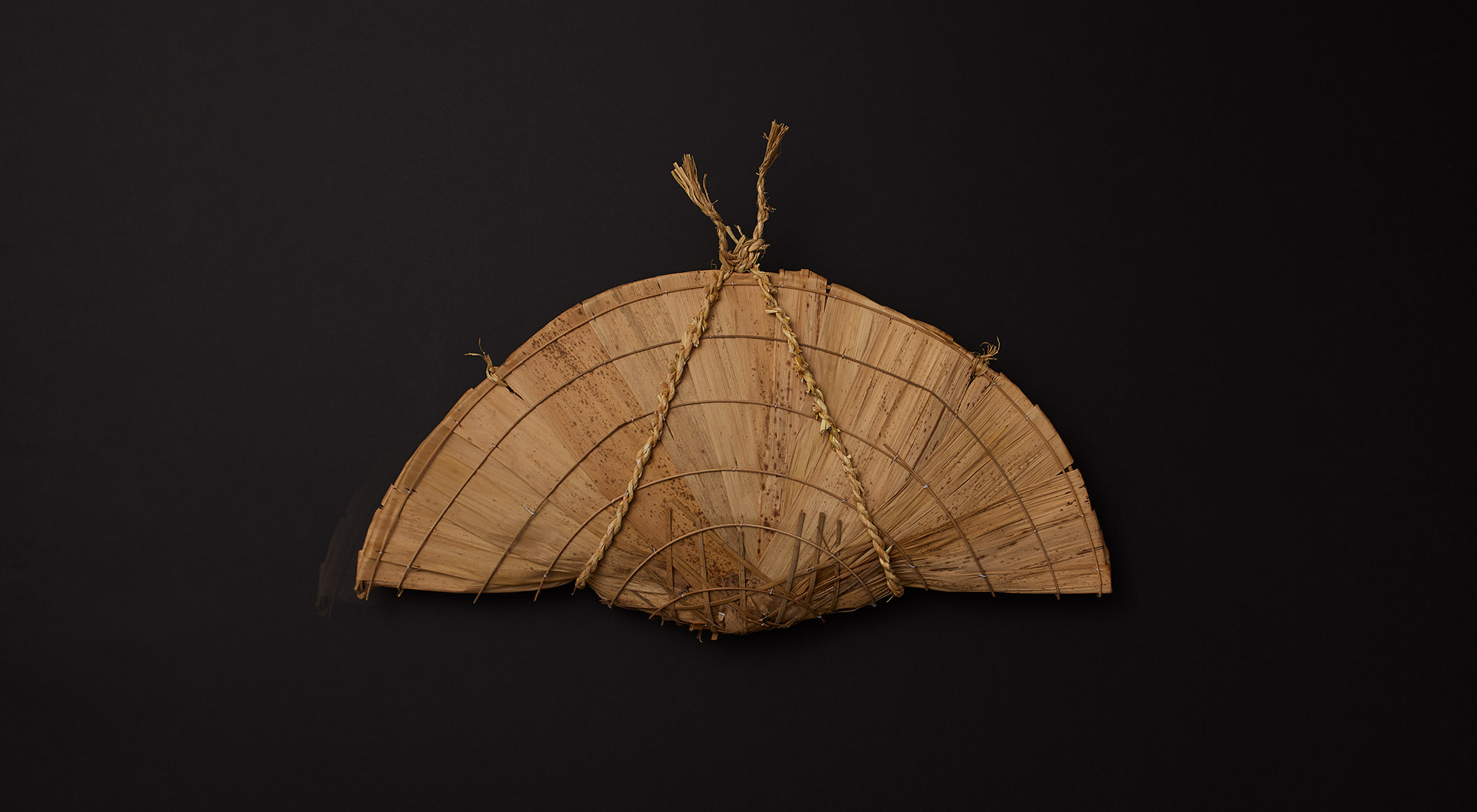
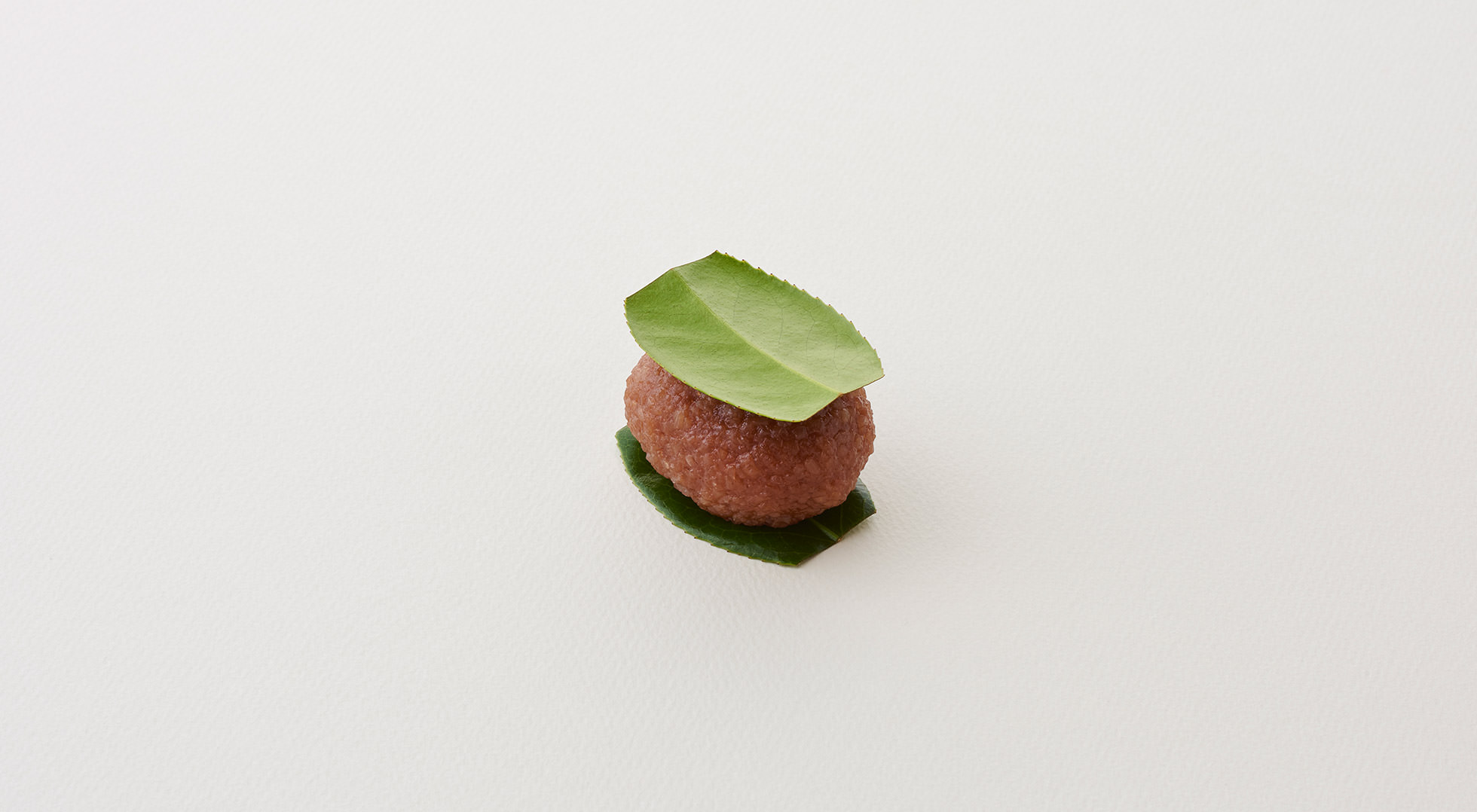
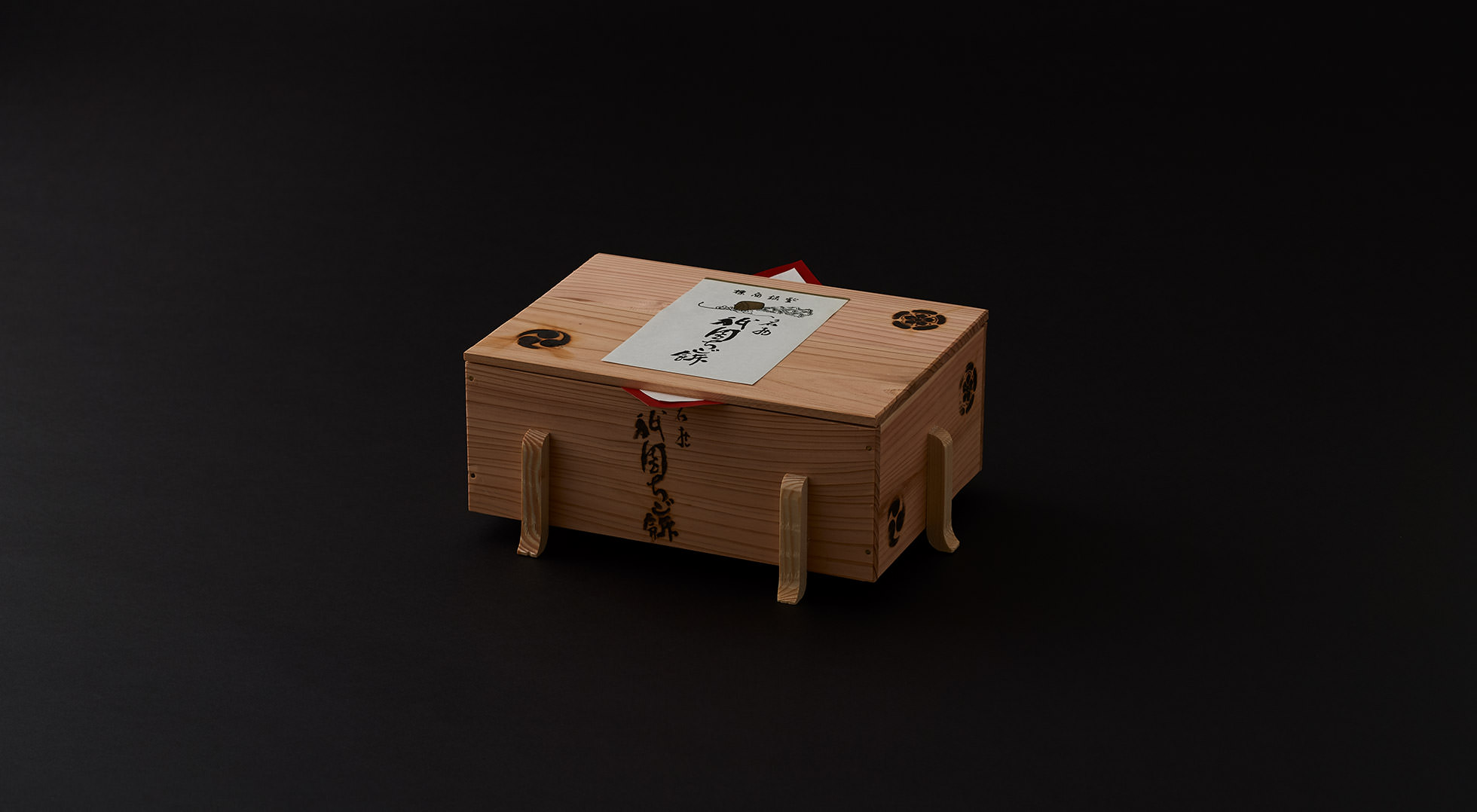
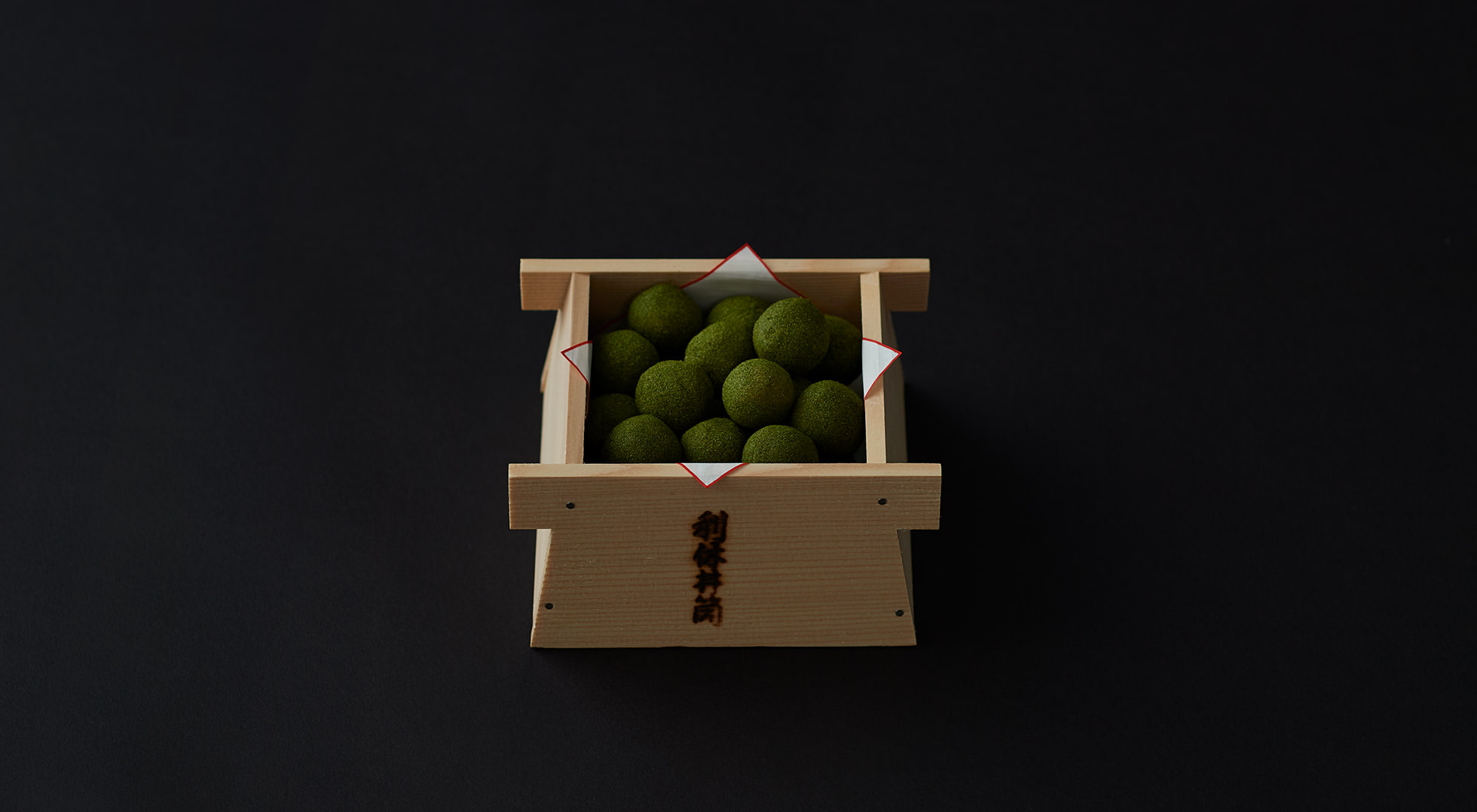
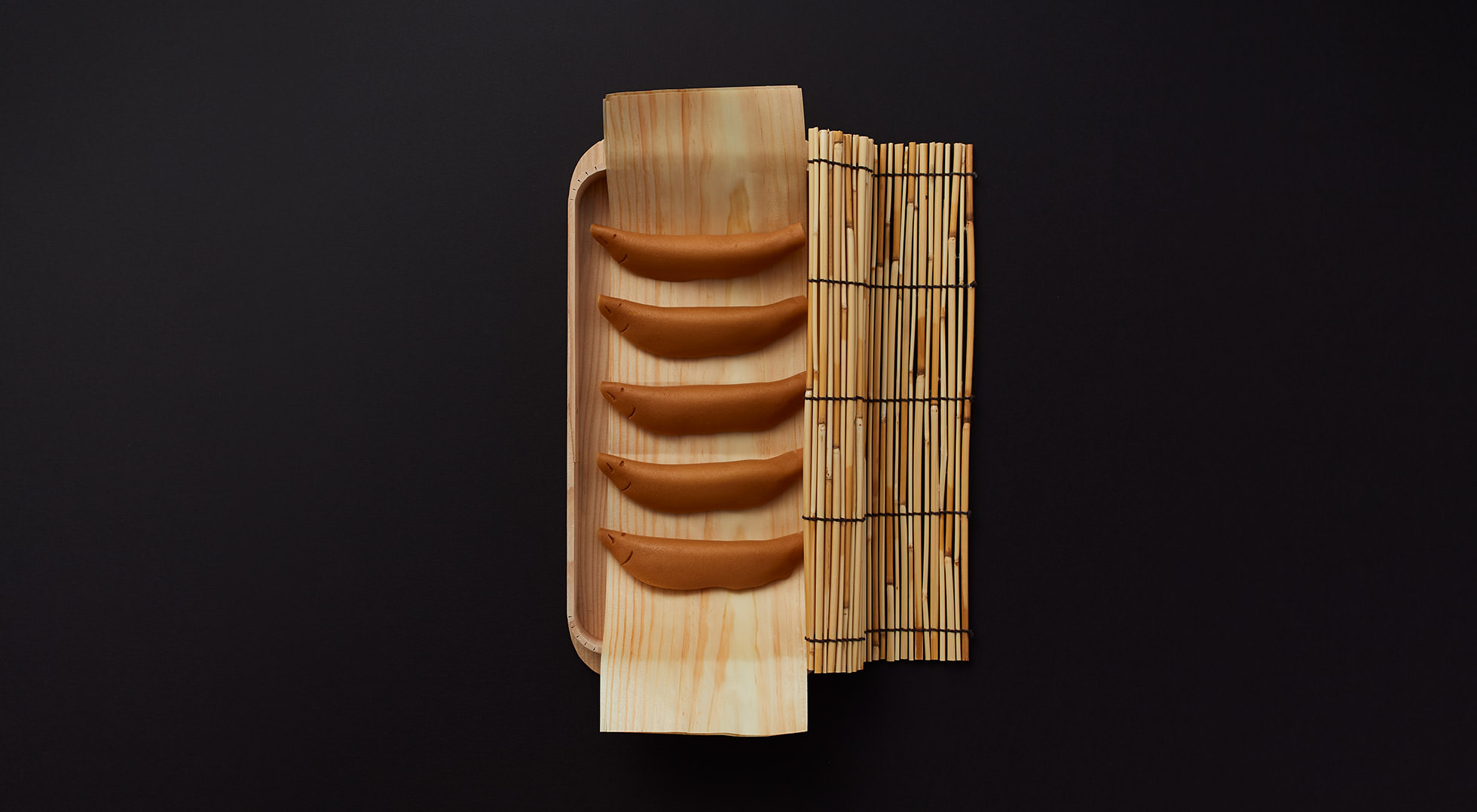
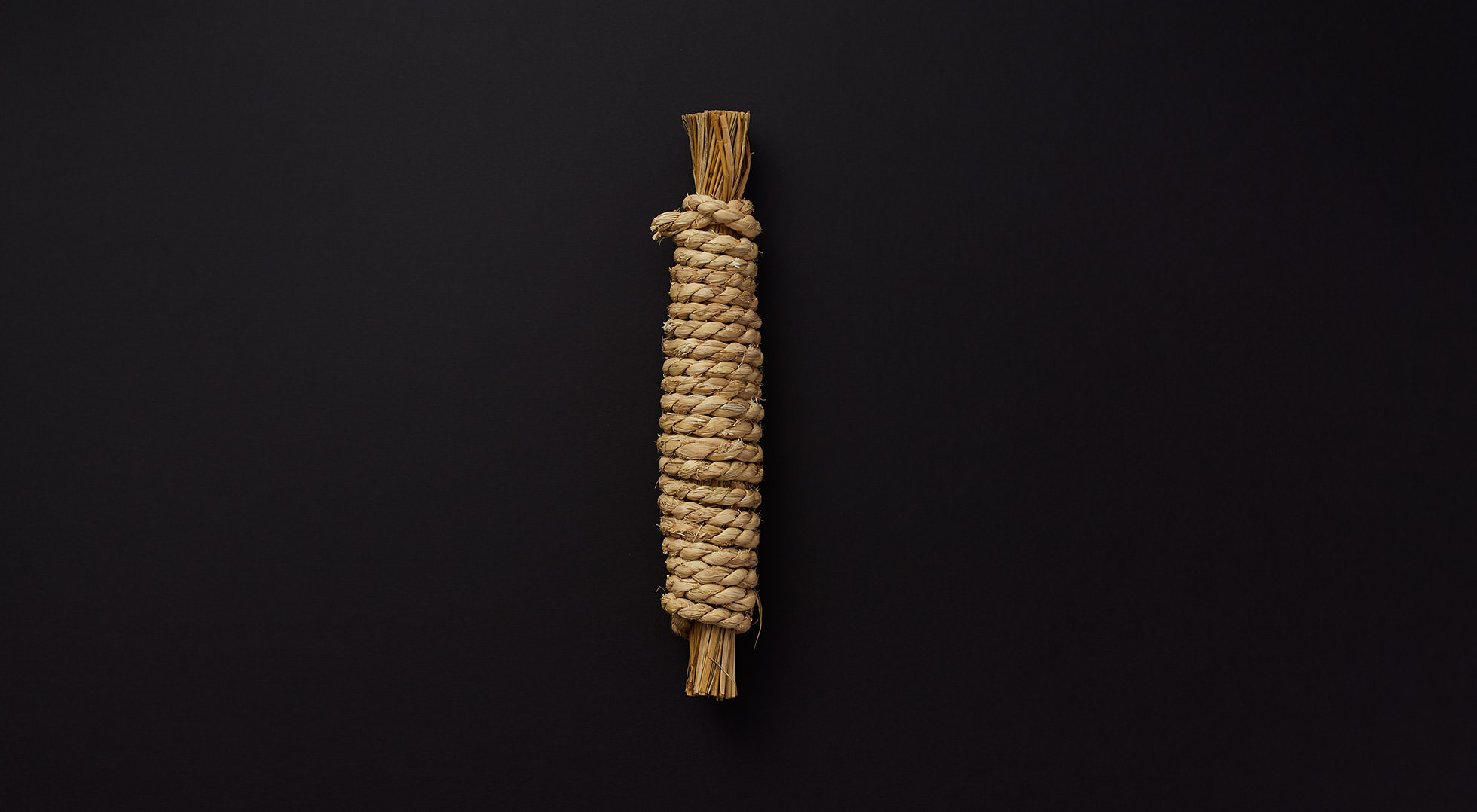
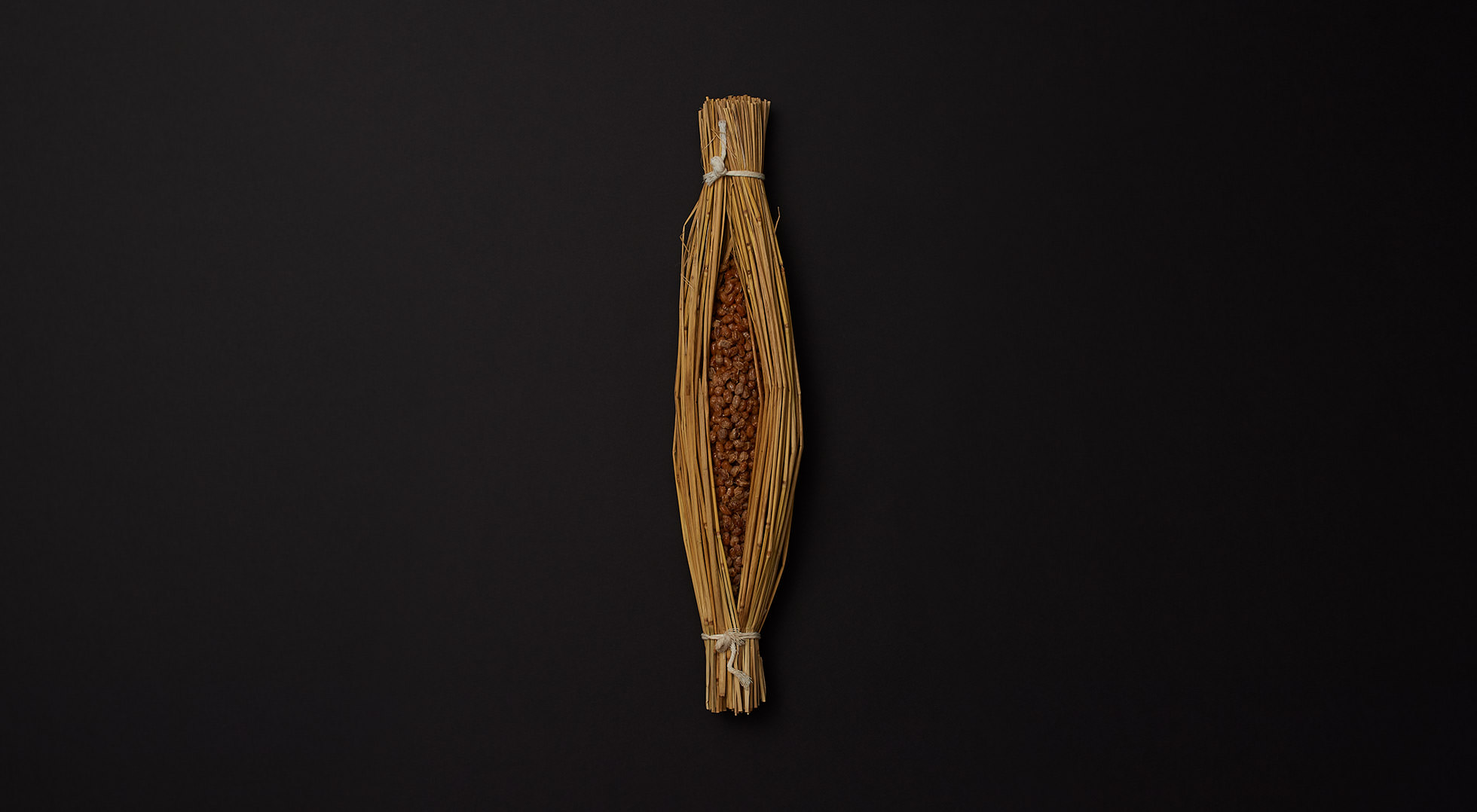
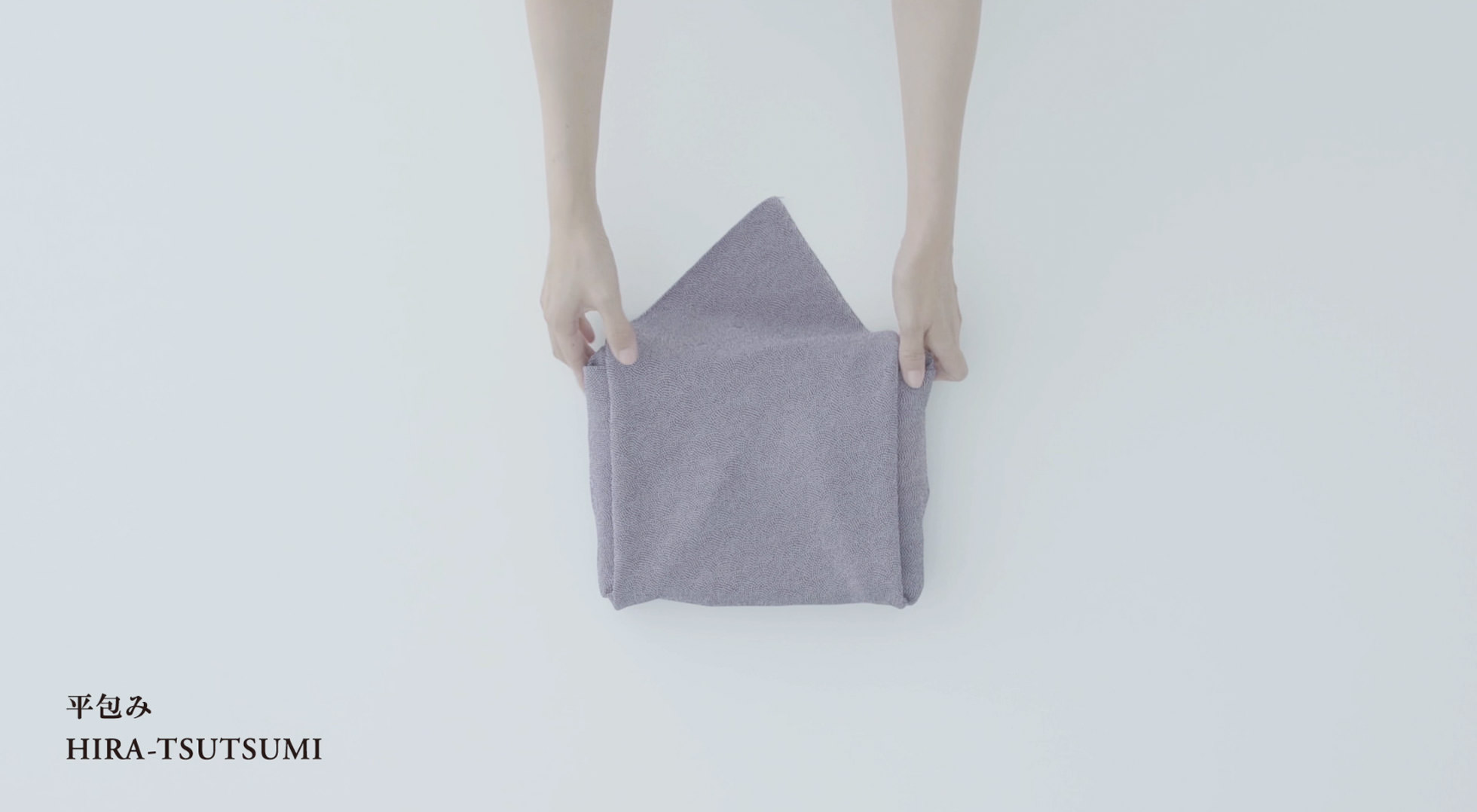
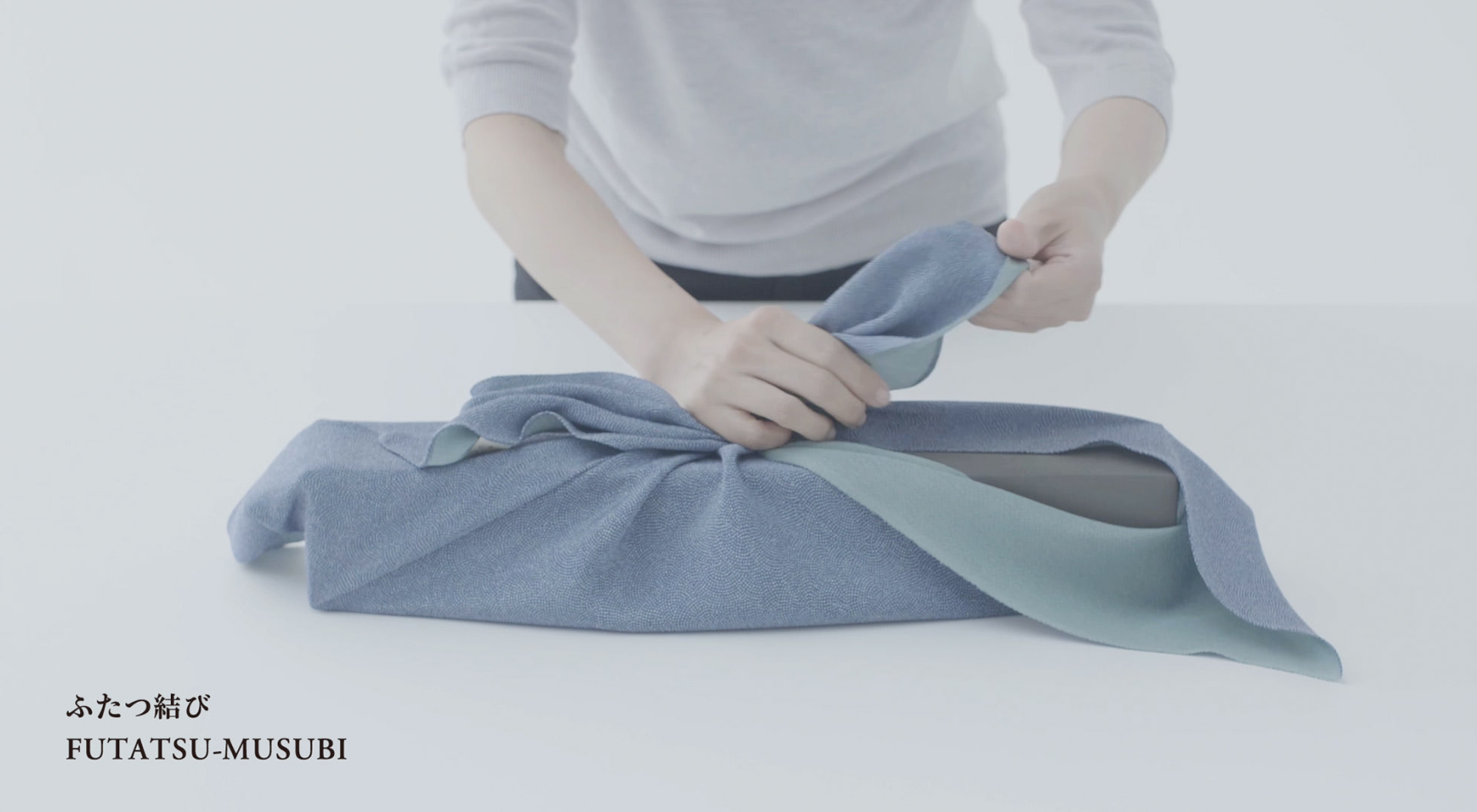
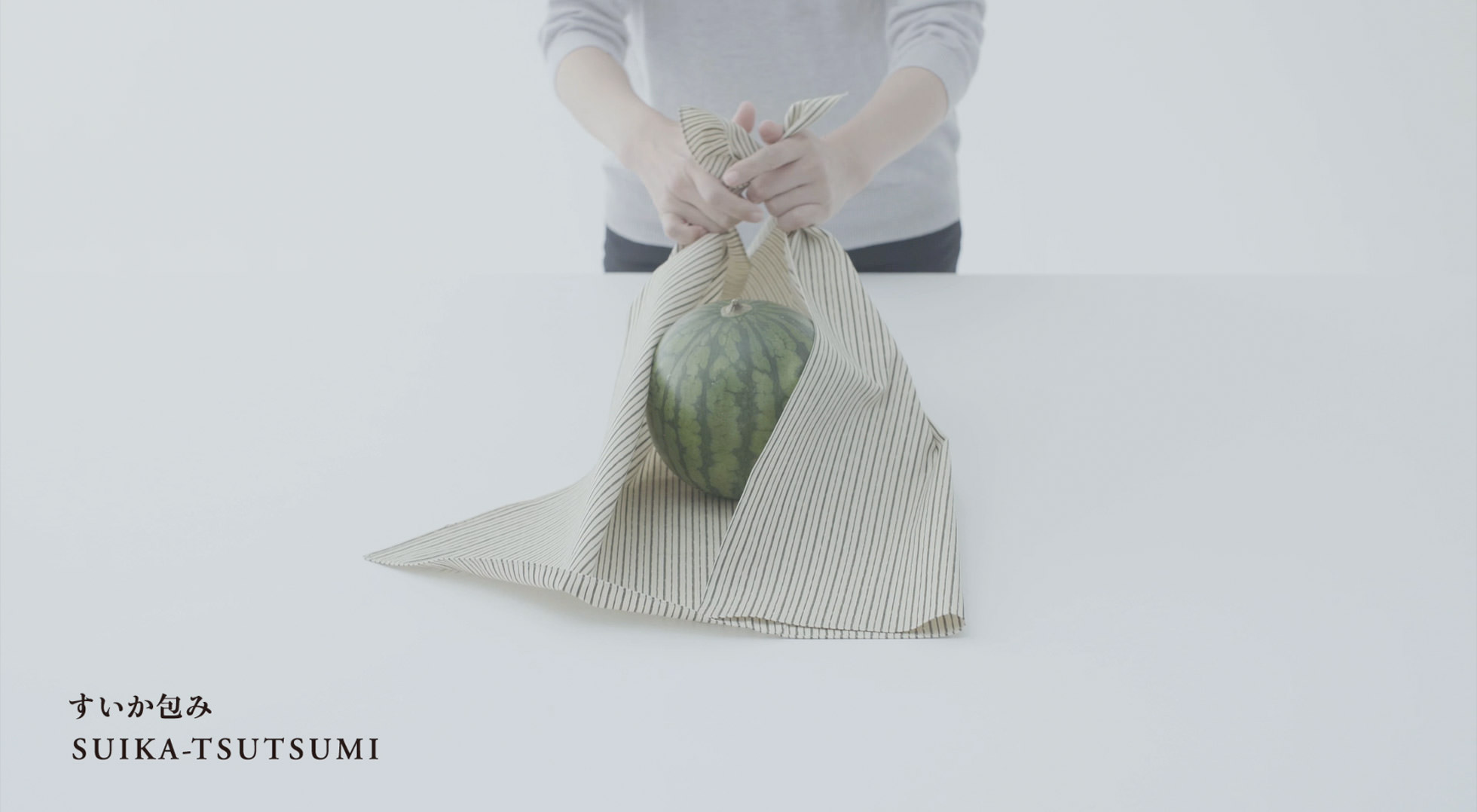
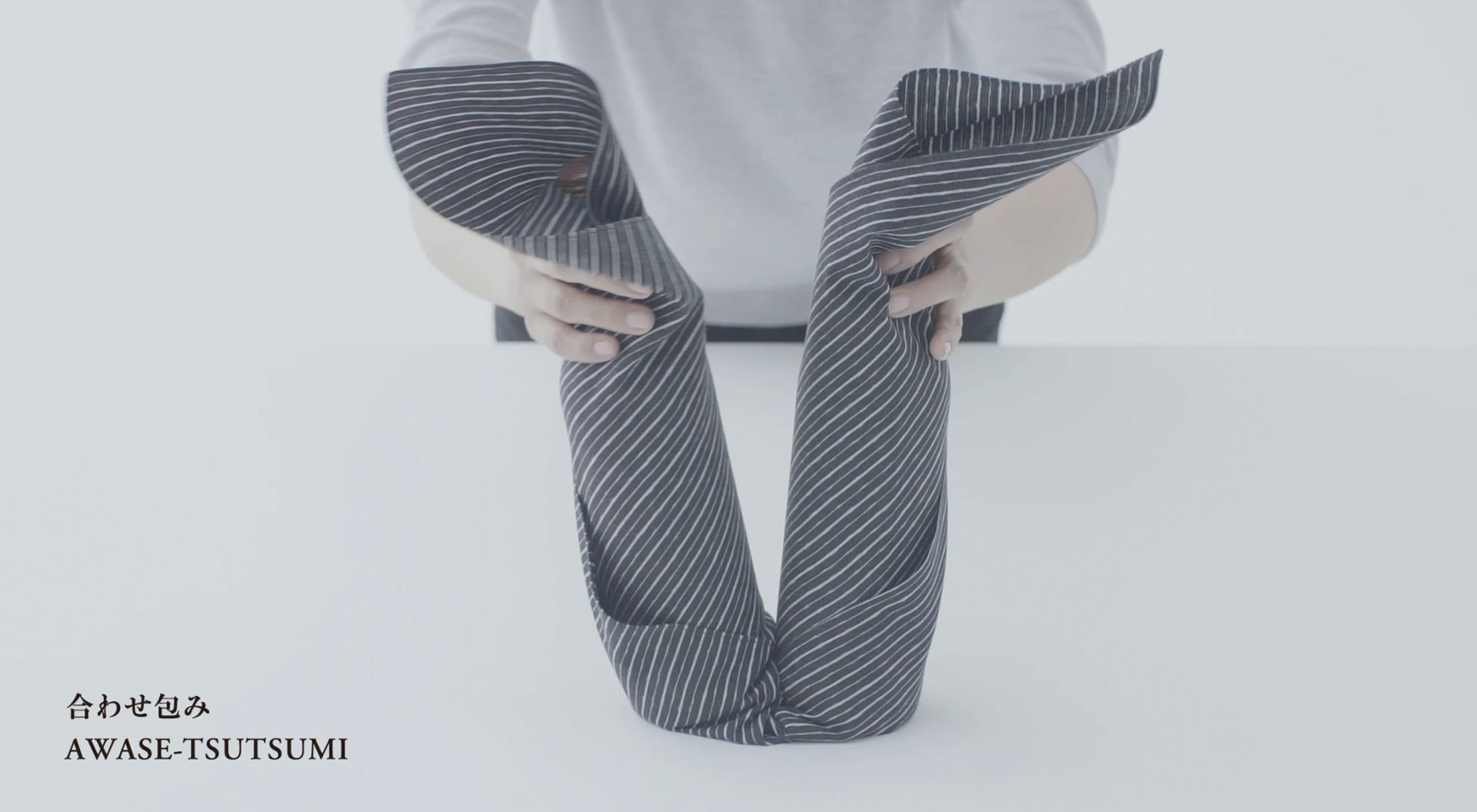
Practical wrapping
The tamago-tsuto protects precious eggs, making it easy to carry and preserve them; the kome-dawara, straw bags for rice, made transport of heavy rice less burdensome; and the cylindrical taru barrels allowed liquids to be carried by rolling. In agrarian times, people used familiar natural materials and their wisdom to wrap foodstuff functionally, to logically strive toward a rich food culture.